Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 )O
)O (
( = Th, Np) prepared by supercritical hydrothermal synthesis
= Th, Np) prepared by supercritical hydrothermal synthesisShirasaki, Kenji*; Tabata, Chihiro*; Sunaga, Ayaki*; Sakai, Hironori; Li, D.*; Konaka, Mariko*; Yamamura, Tomoo*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 563, p.153608_1 - 153608_11, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:50.96(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We focused on the direct synthesis of (U,  )O
)O solid solution (
solid solution ( =Th, Np) by extending our recent progress in hydrothermal synthesis with additives. The homogeneity of the (U,
=Th, Np) by extending our recent progress in hydrothermal synthesis with additives. The homogeneity of the (U,  )O
)O (
( = Th, Np) systems prepared by supercritical hydrothermal reactions was investigated through crystallographic analysis based on Vegard's law, and the
= Th, Np) systems prepared by supercritical hydrothermal reactions was investigated through crystallographic analysis based on Vegard's law, and the  Na nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurement of (U, Np, Na)O
Na nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurement of (U, Np, Na)O solid solutions. Our experimental and analytical results revealed that (i) an optimal additive is ammonium carbonate and starting uranium valence is IV in the case of (U, Th)O
solid solutions. Our experimental and analytical results revealed that (i) an optimal additive is ammonium carbonate and starting uranium valence is IV in the case of (U, Th)O , and (ii) an optimal additive is ethanol and starting uranium valence is VI in the case of (U, Np)O
, and (ii) an optimal additive is ethanol and starting uranium valence is VI in the case of (U, Np)O , for producing the homogeneous solid solutions by hydrothermal synthesis.
, for producing the homogeneous solid solutions by hydrothermal synthesis.
 ; Stoichiometry, crystal shape and size, and homogeneity observed using
; Stoichiometry, crystal shape and size, and homogeneity observed using  Na-NMR spectroscopy of (U, Na)O
Na-NMR spectroscopy of (U, Na)O
Tabata, Chihiro*; Shirasaki, Kenji*; Sunaga, Ayaki*; Sakai, Hironori; Li, D.*; Konaka, Mariko*; Yamamura, Tomoo*
CrystEngComm (Internet), 23(48), p.8660 - 8672, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:63.38(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The hydrothermal synthesis of pure uranium dioxide under supercritical water (SCW) conditions was investigated. The nonstoichiometry, crystallite size and morphology of the UO particles were investigated. The SCW hydrothermal synthesis may be a promising method for producing homogeneous UO
particles were investigated. The SCW hydrothermal synthesis may be a promising method for producing homogeneous UO and its solid solutions with well-defined nonstoichiometries (
and its solid solutions with well-defined nonstoichiometries ( ), shapes, and sizes.
), shapes, and sizes.
Konishi, Satoshi; Nishio, Satoshi; Tobita, Kenji; DEMO Design Team
Fusion Engineering and Design, 63-64, p.11 - 17, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:93.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)The first fusion power plant DEMO must have some reality that ITER and other facilities in the same period are expected to prove its feasibility. The DEMO should also be so attractive and advanced that the future society would be interested in constructing based on its concept. The present DEMO plant concept intends to satisfy these antagonistic requirements assuming construction in 2030s immediately after successful completion of fundamental ITER mission. A steady tokamak is minimized to have 5.8m of major radius with 2.3GW with Q exceeds 30. Modestly ambitious plasma parameters are chosen. Technology improvement is assumed to make maximum 20 T magnet, metal first wall and super critical water cooled ITER-like blanket modules feasible. Tritium inventory is reduced to 1kg with improved safety system concept. This conceptual design identifies various technical issues that are expected to be solved by intensive R&D efforts during ITER period, and indicates a possible step immediately after ITER.
Kakuta, Toshiya*; Hirata, Shingo*; Mori, Seiji*; Konishi, Satoshi; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Nishi, Masataka; Ohara, Yoshihiro
Fusion Science and Technology, 41(3), p.1069 - 1073, 2002/05
Research-and-development of the supercritical water-cooled prototype fusion reactor which has cost competitiveness has been performed in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). It is necessary to establish immediately the design concept of the blanket tritium recovery system which collects tritium continuously and safely from the supercritical water-cooled blanket because fuel self-sufficiency is inevitable in the prototype reactor. The candidate systems are; 1) batch-processing cryogenic molecular sheave bed recovery system with cryogenic temperature operation, 2) continuous processing Pd membrane penetration recovery system with high vacuum operation. In the present study, however, the third candidate system, the hydrogen pump system with protonic conductors, was investigated. As a result of the study, it was made clear that the system with minimized energy consumption and minimized accidental tritium release could be realized by using the hydrogen pump for the blanket tritium recovery system of the prototype fusion reactor.
Konishi, Satoshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 58-59, p.1103 - 1107, 2001/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.06(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Aso, Tomokazu; Kaminaga, Masanori; Terada, Atsuhiko*; Hino, Ryutaro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 43(11), p.1149 - 1158, 2001/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Aso, Tomokazu; Kaminaga, Masanori; Terada, Atsuhiko*; Hino, Ryutaro
JAERI-Conf 2001-002, p.893 - 903, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Aso, Tomokazu; Kaminaga, Masanori; Terada, Atsuhiko*; Hino, Ryutaro
Kashika Joho Gakkai-Shi, 20(Suppl.2), p.175 - 178, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Aso, Tomokazu; Kaminaga, Masanori; Terada, Atsuhiko*; Hino, Ryutaro
JAERI-Tech 2000-018, p.49 - 0, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Aso, Tomokazu; Kaminaga, Masanori; Terada, Atsuhiko*; Ishikura, Shuichi*; Hino, Ryutaro
JAERI-Tech 2000-011, p.23 - 0, 2000/02
no abstracts in English
Inohara, Yasuto*; Ioka, Ikuo; Fukaya, Kiyoshi; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Kuroda, Yuji*; Miyamoto, Satoshi*
Fushoku Boshoku Kyokai Dai-47-Kai Zairyo To Kankyo Toronkai Koenshu (B-204), p.177 - 180, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Aso, Tomokazu; Kaminaga, Masanori; Terada, Atsuhiko; Hino, Ryutaro
JAERI-Tech 99-049, 45 Pages, 1999/06
no abstracts in English
Aso, Tomokazu; Ishikura, Shuichi*; Terada, Atsuhiko*; Teshigawara, Makoto; Watanabe, Noboru; Hino, Ryutaro
Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-7) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 1999/04
no abstracts in English
Aso, Tomokazu; Kaminaga, Masanori; Terada, Atsuhiko; Hino, Ryutaro
JAERI-Tech 99-014, 113 Pages, 1999/03
no abstracts in English
Mochizuki, Yuji
JAERI-Data/Code 99-015, 21 Pages, 1999/03
no abstracts in English
Aso, Tomokazu; Ishikura, Shuichi*; Terada, Atsuhiko; Kai, Tetsuya; Teshigawara, Makoto*; Kaminaga, Masanori; Hino, Ryutaro; Watanabe, Noboru*
Proc. of 14th Meeting of the Int. Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS-14), 2, p.804 - 822, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
Nagaoka, Mika; Fujita, Hiroki; Aida, Taku*; Smith, R.*
no journal, ,
Radioactivity concentration in environmental sample such as leaf, seaweed has been measured through chemical separation with organic matter decomposition and extraction of target element. However, the usual chemical treatment could affect worker's health, chemical hood and surrounding environment by usage of chemical regent. On the other hand, supercritical water reaction could decompose organic matter without health and environmental hazard caused by the regent. Therefore, we have tried to apply the supercritical water reaction to radioactivity analysis of environmental samples. In this research, organic matter content and strontium concentration in environmental sample were compared with between before and after the reaction. The organic matters were highly decomposed with the water reaction at higher temperature and for longer reaction time. However the strontium was not extracted into solution after the reaction.
Nagaoka, Mika; Fujita, Hiroki; Aida, Taku*; Smith, R.*
no journal, ,
The conventional pretreatment of radioactive nuclides of beta-ray emitters ( Sr) and alpha-ray sources (U,
Sr) and alpha-ray sources (U,  Pu,
Pu, 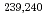 Pu,
Pu,  Am) in the environmental and bioassay samples is performed with much chemical regents to mineralize of organic matters and extract target nuclides. The mineralization of organic matter is both time-consuming and inefficient and it requires a large quantity of acid reagents that are toxic. On the other hand, supercritical water (SCW) can decompose organic matters without chemical regents. Therefore, in this research, the SCW was applied for decomposition of environmental and bioassay samples.
Am) in the environmental and bioassay samples is performed with much chemical regents to mineralize of organic matters and extract target nuclides. The mineralization of organic matter is both time-consuming and inefficient and it requires a large quantity of acid reagents that are toxic. On the other hand, supercritical water (SCW) can decompose organic matters without chemical regents. Therefore, in this research, the SCW was applied for decomposition of environmental and bioassay samples.